Ships: 1-2 business days
Product Specific References for Applications and Species
- ELISA: Mouse
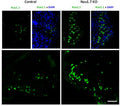
- Immunocytochemistry: Mouse | Rat
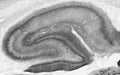
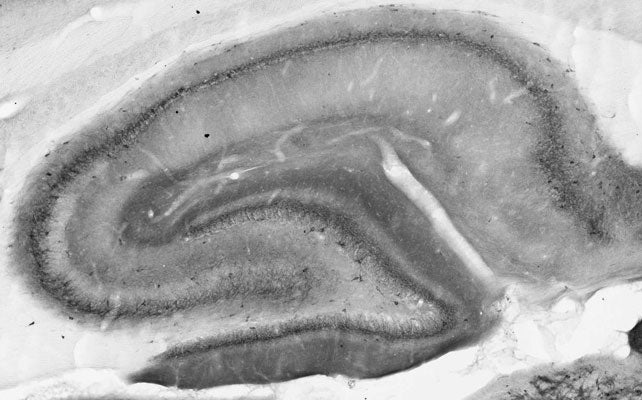
- Immunohistochemistry: Human | Mouse | Non-Human Primate | Rat
- MSD: Mouse
- Western Blot: Mouse | Rat
- Additional Publications: Unspecified
| ELISA: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 33732797 | 1:200 | Han, Z., et al. 2021. Relative Quantification of NaV1. 1 Protein in Mouse Brains Using a Meso Scale Discovery-Electrochemiluminescence (MSD-ECL) Method. . Bio-protocol, e3910-e3910. |
| 32848094 | 1:200 | Han, Z., et al. 2020. Antisense oligonucleotides increase Scn1a expression and reduce seizures and SUDEP incidence in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. . Science translational medicine, eaaz6100. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28931427 | not listed | Hu, L., et al. 2017. Serotonin 5-HT6 receptors affect cognition in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by regulating cilia function.. Alzheimers Research and Therapy, 76. |
| 25561543 | 1:400 | Freeman, S.A., et al. 2015. Acceleration of conduction velocity linked to clustering of nodal components precedes myelination. . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, E321-E328. |
| 20133873 | 1:100 | Brackenbury, W.J., et al. 2010. Functional reciprocity between Na+ channel Nav1. 6 and β1 subunits in the coordinated regulation of excitability and neurite outgrowth. . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2283-2288. |
| 19013247 | 1:100-1:250 | O'Malley, H.A., et al. 2009. Loss of Na+ channel β2 subunits is neuroprotective in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 143-155. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 25561543 | 1:400 | Freeman, S.A., et al. 2015. Acceleration of conduction velocity linked to clustering of nodal components precedes myelination. . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, E321-E328. |
| 21118538 | not listed | Persson, A.K., et al. 2010. Sodium-calcium exchanger and multiple sodium channel isoforms in intra-epidermal nerve terminals. . Molecular Pain, 1744-8069. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Human | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 24107939 | 1:100–1:1000 | Puthussery, T., et al. 2013. NaV1. 1 channels in axon initial segments of bipolar cells augment input to magnocellular visual pathways in the primate retina. . Journal of Neuroscience, 16045-16059. |
| 20147455 | 1:100 | Black, J.A., et al. 2010. Astrocytes within multiple sclerosis lesions upregulate sodium channel Nav1. 5. . Brain, 835-846. |
| 18442883 | 1:200 | Zhao, P., et al. 2008. Voltage-gated sodium channel expression in rat and human epidermal keratinocytes: evidence for a role in pain. . Pain, 90-105. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 39559752 | 1:250 | Iseppon, F, et al. 2024. Sodium channels Nav1.7, Nav1.8 and pain; two distinct mechanisms for Nav1.7 null analgesia. Neurobiology of Pain, 100168. |
| 38443186 | 1:500 | Liebergall, SR, et al. 2024. Ndnf Interneuron Excitability Is Spared in a Mouse Model of Dravet Syndrome. The Journal of Neuroscience, 0. |
| 35354025 | not listed | Kaneko, K., et al. 2022. Developmentally regulated impairment of parvalbumin interneuron synaptic transmission in an experimental model of Dravet syndrome.. Cell reports, 110580. |
| 35219855 | 1:200 | Studtmann C., et al. 2022. NaV1.1 haploinsufficiency impairs glutamatergic and GABAergic neuron function in the thalamus.. Neurobiology of disease, 105672. |
| 33910599 | 1:100 | Haigh, J.L., et al. 2021. Deletion of a non-canonical regulatory sequence causes loss of Scn1a expression and epileptic phenotypes in mice.. Genome Medicine, 69. |
| 31933626 | 1:500 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2019. Changes in the Fluorescence Tracking of NaV1.6 Protein Expression in a BTBR T+Itpr3tf/J Autistic Mouse Model.. Neural Plasticity, 4893103. |
| 31354436 | 1:200 | Yang, J., et al. 2019. Biophysical properties of somatic and axonal voltage-gated sodium channels in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. . Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 17. |
| 31282864 | 1:500 | Goff, K.M., et al. 2019. Vasoactive intestinal peptide-expressing interneurons are impaired in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome.. Elife, e46846. |
| 31201232 | 1:200 | Hosoi, N., et al. 2019. Deletion of Class II ADP-Ribosylation Factors in Mice Causes Tremor by the Nav1.6 Loss in Cerebellar Purkinje Cell Axon Initial Segments.. Journal of Neuroscience, 6339-6353. |
| 30125271 | not listed | Nunes, D., et al. 2018. Axonal sodium channel NaV1. 2 drives granule cell dendritic GABA release and rapid odor discrimination. . PLoS biology, e2003816. |
| 26909021 | 1:500 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2016. Improved methods for fluorescence microscopy detection of macromolecules at the axon initial segment. . Frontiers in cellular neuroscience, 5. |
| 23891806 | 1:1000 | Xiao, M., et al. 2013. FGF14 localization and organization of the axon initial segment. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 393-403. |
| 23311867 | 1:200 | Papale, L.A., et al. 2013. Altered sleep regulation in a mouse model of SCN1A‐derived genetic epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+).. Epilepsia, 625-634. |
| 21676499 | 1:300 | Wykes, R., et al. 2012. Changes in the physiology of CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons in preplaque CRND8 mice. . Neurobiology of aging, 1609-1623. |
| 21994381 | 1:4000 | Wu, C., et al. 2011. Action potential generation at an axon initial segment-like process in the axonless retinal AII amacrine cell. . Journal of Neuroscience, 14654-14659. |
| 21190943 | 1:20 | Kim, D.Y., et al. 2011. Reduced sodium channel Nav1. 1 levels in BACE1-null mice. . Journal of Biological Chemistry, 8106-8116. |
| 20628201 | not listed | Wimmer, V.C., et al. 2010. Axon initial segment dysfunction in a mouse model of genetic epilepsy with febrile seizures plus. . The Journal of clinical investigation, 2661-2671. |
| 20375142 | not listed | Wimmer, V.C., et al. 2010. Axon initial segment dysfunction in epilepsy. . The Journal of physiology, 1829-1840. |
| 18621130 | not listed | Duflocq, A., et al. 2008. Nav1. 1 is predominantly expressed in nodes of Ranvier and axon initial segments. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 180-192. |
| 17884088 | 1:50 | Lopez-Santiago, L.F., et al. 2007. Sodium channel Scn1b null mice exhibit prolonged QT and RR intervals. . Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 636-647. |
| 17122053 | 1:1000 | Burkhalter, A., et al. 2006. Differential expression of I(A) channel subunits Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 in mouse visual cortical neurons and synapses.. Journal of Neuroscience, 12274-82. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Non-Human Primate | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 24107939 | 1:100–1:1000 | Puthussery, T., et al. 2013. NaV1. 1 channels in axon initial segments of bipolar cells augment input to magnocellular visual pathways in the primate retina. . Journal of Neuroscience, 16045-16059. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 26888923 | not listed | Kim, K.X., et al. 2016. Maturation of NaV and KV channel topographies in the auditory nerve spike initiator before and after developmental onset of hearing function. . Journal of Neuroscience, 2111-2118. |
| 25294986 | 1:200 | Tian, C., et al. 2014. Molecular identity of axonal sodium channels in human cortical pyramidal cells. . Frontiers in cellular neuroscience, 297. |
| 24077057 | 1:5000 | Vega, A.V., et al. 2013. Interaction between the transcriptional corepressor Sin3B and voltage-gated sodium channels modulates functional channel expression. . Scientific Reports, 1-8. |
| 21734302 | 1:200 | Lysakowski, A., et al. 2011. Molecular microdomains in a sensory terminal, the vestibular calyx ending.. Journal of Neuroscience, 10101-10114. |
| 21569247 | 1:100 | Ahn, H.S., et al. 2011. Nav1. 7 is the predominant sodium channel in rodent olfactory sensory neurons. . Molecular pain, 1744-8069. |
| 19118165 | 1:250 | Lorincz, A., et al. 2008. Cell-type-dependent molecular composition of the axon initial segment. . Journal of Neuroscience, 14329-14340. |
| 18769561 | 1:500-1:1000 | Mojumder, D.K., et al. 2008. Subcellular compartmentalization of two calcium binding proteins, calretinin and calbindin-28 kDa, in ganglion and amacrine cells of the rat retina. . Molecular Vision, 1600. |
| 18442883 | 1:200 | Zhao, P., et al. 2008. Voltage-gated sodium channel expression in rat and human epidermal keratinocytes: evidence for a role in pain. . Pain, 90-105. |
| Meso Scale Discovery: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 32647108 | 1:200 | Kian Huat Lim, et al. 2020. Antisense oligonucleotide modulation of non-productive alternative splicing upregulates gene expression.. Nature Communications, 3501. |
| Western Blot: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 37833406 | not listed | Ma, D, et al. 2023. A cytoskeleton-membrane interaction conserved in fast-spiking neurons controls movement, emotion, and memory. Molecular psychiatry, . |
| 36459557 | not listed | Morey, N., et al. 2022. Treatment of Epilepsy Using a Targeted p38γ Kinase Gene Therapy. Science Advances, eadd2577. |
| 35219855 | 1:1000 | Studtmann C., et al. 2022. NaV1.1 haploinsufficiency impairs glutamatergic and GABAergic neuron function in the thalamus.. Neurobiology of disease, 105672. |
| 33732797 | not listed | Han, Z., et al. 2021. Relative Quantification of NaV1. 1 Protein in Mouse Brains Using a Meso Scale Discovery-Electrochemiluminescence (MSD-ECL) Method. . Bio-protocol, e3910-e3910. |
| 32848094 | not listed | Han, Z., et al. 2020. Antisense oligonucleotides increase Scn1a expression and reduce seizures and SUDEP incidence in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. . Science translational medicine, eaaz6100. |
| 31830809 | 1:1000 | Niibori, Y., et al. 2020. Sexually divergent mortality and partial phenotypic rescue after gene therapy in a mouse model of dravet syndrome. . Human gene therapy, 339-351. |
| 31933626 | 1:500 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2019. Changes in the Fluorescence Tracking of NaV1.6 Protein Expression in a BTBR T+Itpr3tf/J Autistic Mouse Model.. Neural Plasticity, 4893103. |
| 31308096 | 1:1000 | Gomez, C.D., et al. 2019. Early life inflammation increases CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability in a sex and age dependent manner through a chloride homeostasis disruption. . Journal of Neuroscience, 7244-7259. |
| 30125271 | not listed | Nunes, D., et al. 2018. Axonal sodium channel NaV1. 2 drives granule cell dendritic GABA release and rapid odor discrimination. . PLoS biology, e2003816. |
| 29956586 | 1:500 | Dash, B., et al. 2018. Nonmuscle myosin II isoforms interact with sodium channel alpha subunits. . Molecular pain, 1744806918788638. |
| 26889602 | 1:1000 | Bosch, M.K., et al. 2016. Proteomic analysis of native cerebellar iFGF14 complexes.. Channels , 297-312. |
| 25203314 | 1:200 | Li, T., et al. 2014. Action potential initiation in neocortical inhibitory interneurons. . PLoS Biology, e1001944. |
| 23891806 | 1:1000 | Xiao, M., et al. 2013. FGF14 localization and organization of the axon initial segment. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 393-403. |
| 22131424 | 1:500 | Kaphzan, H., et al. 2011. Alterations in intrinsic membrane properties and the axon initial segment in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome.. Journal of Neuroscience, 17637-17648. |
| 19013247 | 1:100-1:250 | O'Malley, H.A., et al. 2009. Loss of Na+ channel β2 subunits is neuroprotective in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 143-155. |
| 18621130 | not listed | Duflocq, A., et al. 2008. Nav1. 1 is predominantly expressed in nodes of Ranvier and axon initial segments. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 180-192. |
| Western Blot: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 19692609 | 1:500 | von Reyn, C.R., et al. 2009. Calpain mediates proteolysis of the voltage-gated sodium channel α-subunit. . Journal of Neuroscience, 10350-10356. |
| 19411284 | not listed | Tobin, A.A., et al. 2009. Loss of cerebrovascular Shaker-type K+ channels: a shared vasodilator defect of genetic and renal hypertensive rats. . American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, H293-H303. |
| Additional Publications: Unspecified | ||
| PMID | Publication | |
| 25421039 | Wimmer, V.C., et al. 2015. Sodium channel β1 subunit localizes to axon initial segments of excitatory and inhibitory neurons and shows regional heterogeneity in mouse brain. . Journal of Comparative Neurology, 814-830. | |
| 18601978 | Vega, A.V., et al. 2008. Reduced expression of Nav1. 6 sodium channels and compensation by Nav1. 2 channels in mice heterozygous for a null mutation in Scn8a. . Neuroscience letters, 69-73. | |
| 18079688 | Mojumder, D.K., et al. 2007. Voltage-gated sodium channel alpha-subunits Na (v) 1.1, Na (v) 1.2, and Na (v) 1.6 in the distal mammalian retina. . Molecular Vision, 2163-2182. | |
| 17111377 | Van Wart, A., et al. 2007. Polarized distribution of ion channels within microdomains of the axon initial segment. . Journal of Comparative Neurology, 339-352. | |