Ships: 1-2 business days
Product Specific References for Applications and Species
- Immunocytochemistry: Mouse | Marine Mollusk | Rat
- Immunohistochemistry: Mouse | Rat
- Immunoprecipitation: Human | Mouse
- Western Blot: Mouse | Rat
| Immunocytochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 38457342 | not listed | Wu, J, et al. 2024. Disease-causing Slack potassium channel mutations produce opposite effects on excitability of excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Cell Reports, 113904. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Marine Mollusk | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 23115170 | 1:1000 | Zhang, Y., et al. 2012. Regulation of neuronal excitability by interaction of fragile X mental retardation protein with slack potassium channels.. Journal of Neuroscience, 15318-15327. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28982974 | 1:250 | Gururaj, S., et al. 2017. Protein kinase A-induced internalization of Slack channels from the neuronal membrane occurs by adaptor protein-2/clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 19304-19314. |
| 27091544 | 1:50 | Bansal, V., et al. 2016. Na(+) -Activated K(+) Channels in Rat Supraoptic Neurones. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, . |
| 23466807 | 1:200 | Cervantes, B., et al. 2013. Identity, expression and functional role of the sodium-activated potassium current in vestibular ganglion afferent neurons.. Neuroscience, 163-175. |
| 19403831 | 2.6ug/ml | Chen, H., et al. 2009. The N-terminal domain of Slack determines the formation and trafficking of Slick/Slack heteromeric sodium-activated potassium channels.. Journal of Neuroscience, 5654-5665. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 38289338 | 1:100 | Yuan, T, et al. 2024. Coupling of Slack and NaV1.6 sensitizes Slack to quinidine blockade and guides anti-seizure strategy development. Elife, RP87559. |
| 37889366 | 1:200 | Wu, J, et al. 2024. Interaction Between HCN and Slack Channels Regulates mPFC Pyramidal Cell Excitability in Working Memory Circuits. Molecular Neurobiology, 2430-2445. |
| 35626730 | 1:500 | Zhou, F., et al. 2022. Slack Potassium Channels Modulate TRPA1-Mediated Nociception in Sensory Neurons. Cells, . |
| 35359569 | 1:400 | Liu, Y., et al. 2022. The Slack Channel Deletion Causes Mechanical Pain Hypersensitivity in Mice. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 811441. |
| 35346832 | 1:400 | Gertler, T.S., et al. 2022. KNa1.1 gain-of-function preferentially dampens excitability of murine parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Neurobiology of disease, 105713. |
| 33817875 | 1:100-1:200 | Ehinger, R., et al. 2021. Slack K+ channels attenuate NMDA‐induced excitotoxic brain damage and neuronal cell death.. The FASEB Journal, e21568. |
| 33401689 | 1:400 | Lu, R., et al. 2021. Functional Coupling of Slack Channels and P2X3 Receptors Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Processing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 405. |
| 26587966 | 1:400 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2016. Differential distribution of the sodium-activated potassium channels slick and slack in mouse brain.. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 2093-2116. |
| 29124216 | 1:200 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2015. Identification of potential novel interaction partners of the sodium-activated potassium channels Slick and Slack in mouse brain. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 291-298. |
| 25609627 | 1:400 | Lu, R., et al. 2015. Slack channels expressed in sensory neurons control neuropathic pain in mice.. Journal of Neuroscience, 1125-1135. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 23872594 | 1:1000 | Huang, F., et al. 2013. TMEM16C facilitates Na(+)-activated K+ currents in rat sensory neurons and regulates pain processing.. Nature Neuroscience, 1284-1290. |
| 23466807 | 1:200 | Cervantes, B., et al. 2013. Identity, expression and functional role of the sodium-activated potassium current in vestibular ganglion afferent neurons.. Neuroscience, 163-175. |
| Immunoprecipitation: Human | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 38289338 | 5ug | Yuan, T, et al. 2024. Coupling of Slack and NaV1.6 sensitizes Slack to quinidine blockade and guides anti-seizure strategy development. eLife, . |
| Immunoprecipitation: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 38289338 | 5ug | Yuan, T, et al. 2024. Coupling of Slack and NaV1.6 sensitizes Slack to quinidine blockade and guides anti-seizure strategy development. eLife, . |
| 29124216 | 40ug | Rizzi, S., et al. 2015. Identification of potential novel interaction partners of the sodium-activated potassium channels Slick and Slack in mouse brain. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 291-298. |
| Western Blot: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 39102831 | 1:600 | Roslan, A., et al. 2024. Slack K+ channels confer protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovascular Research, . |
| 36173683 | 8ug/ml | Burbano, L.E., et al. 2022. Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy for KCNT1 Encephalopathy. JCI Insight, e146090. |
| 35359569 | 1:1000 | Liu, Y., et al. 2022. The Slack Channel Deletion Causes Mechanical Pain Hypersensitivity in Mice. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 811441. |
| 35359569 | 1:1000 | Liu, Y., et al. 2022. The Slack Channel Deletion Causes Mechanical Pain Hypersensitivity in Mice. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 811441. |
| 35197318 | 1:1000 | Zhang, Q., et al. 2022. The Slack Channel Regulates Anxiety-like Behaviors via Basolateral Amygdala Glutamatergic Projections to Ventral Hippocampus. The Journal of Neuroscience, 3049-3064. |
| 30860870 | 1:500 | Pryce, K.D., et al. 2019. Magi-1 scaffolds NaV1.8 and Slack KNa channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons regulating excitability and pain. FASEB, 7315-7330. |
| 28982974 | not listed | Gururaj, S., et al. 2017. Protein kinase A-induced internalization of Slack channels from the neuronal membrane occurs by adaptor protein-2/clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 19304-19314. |
| 28943756 | 1:1000 | Tomasello, D.L., et al. 2017. Slick (Kcnt2) Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Limit Peptidergic Nociceptor Excitability and Hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, . |
| 26587966 | 1:3000 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2016. Differential distribution of the sodium-activated potassium channels slick and slack in mouse brain.. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 2093-2116. |
| 29124216 | 1:3000 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2015. Identification of potential novel interaction partners of the sodium-activated potassium channels Slick and Slack in mouse brain. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 291-298. |
| 26559620 | not listed | Martinez-Espinosa, P.L., et al. 2015. Knockout of Slo2.2 enhances itch, abolishes KNa current, and increases action potential firing frequency in DRG neurons.. Elife, e10013. |
| 25609627 | 1:500 | Lu, R., et al. 2015. Slack channels expressed in sensory neurons control neuropathic pain in mice.. Journal of Neuroscience, 1125-1135. |
| 22145034 | not listed | Wojtovich, A.P., et al. 2011. SLO-2 is cytoprotective and contributes to mitochondrial potassium transport.. PLoS One, e28287. |
| 26845140 | not listed | Wojtovich, A.P., et al. 2016. Cardiac Slo2.1 Is Required for Volatile Anesthetic Stimulation of K+ Transport and Anesthetic Preconditioning.. Anesthesiology, 1065-1076. |
| Western Blot: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28943756 | 1:1000 | Tomasello, D.L., et al. 2017. Slick (Kcnt2) Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Limit Peptidergic Nociceptor Excitability and Hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, . |
| 28366665 | 1:2000 | Evely, K.M., et al. 2017. The Phe932Ile mutation in KCNT1 channels associated with severe epilepsy, delayed myelination and leukoencephalopathy produces a loss-of-function channel phenotype. Neuroscience, 65-70. |
| 27091544 | 1:500 | Bansal, V., et al. 2016. Na(+) -Activated K(+) Channels in Rat Supraoptic Neurones. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, . |
| 26721627 | not listed | Gururaj, S., et al. 2016. Slack sodium-activated potassium channel membrane expression requires p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation.. Neuropharmacology, 279-289. |
| 23872594 | 1:1000 | Huang, F., et al. 2013. TMEM16C facilitates Na(+)-activated K+ currents in rat sensory neurons and regulates pain processing.. Nature Neuroscience, 1284-1290. |
| 20962237 | not listed | Nuwer, M.O., et al. 2010. PKA-induced internalization of slack KNa channels produces dorsal root ganglion neuron hyperexcitability.. Journal of Neuroscience, 14165-14172. |

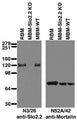
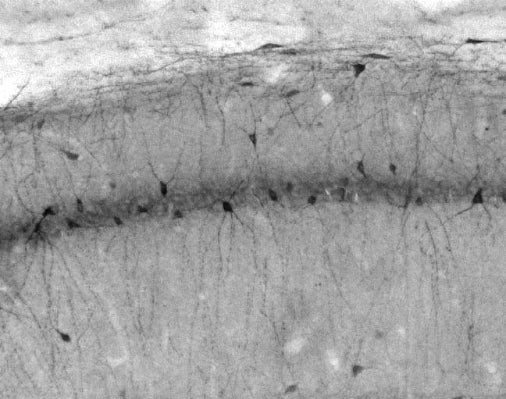
![Immunoblot against brain membranes from adult rat (RBM), mouse (MBM) or human cerebral cortex [HBM(Cx)] or hippocampus [HBM(H)] probed with N3/26 (left) or N52A/42 (right) TC supe.](http://www.antibodiesinc.com/cdn/shop/files/73-051-n3-26-wb-1_120x120.jpg?v=1743797071)