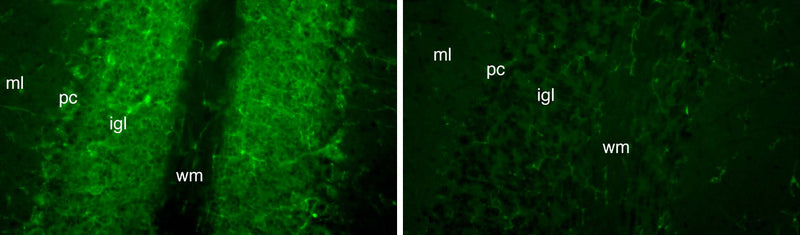
Ships: 1-2 business days
Product Specific References for Applications and Species
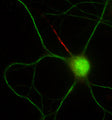
- Immunocytochemistry: Human | Mouse | Rat
- Immunohistochemistry: Human | Mouse | Non-Human Primate | Rat
- Immunoprecipitation: Mouse
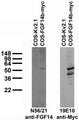
- Western Blot: Human | Mouse
| Immunocytochemistry: Human | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 35441593 | 1:200 | Xiao, Y., et al. 2022. A-type FHFs mediate resurgent currents through TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium channels. Elife, e77558. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 36552754 | 1:500 | Katoshevski, T., et al. 2022. CKII Control of Axonal Plasticity Is Mediated by Mitochondrial Ca2+ via Mitochondrial NCLX. Cells, 3990. |
| 36311018 | 1:500 | Bar, L., et al. 2022. Excitatory and inhibitory hippocampal neurons differ in their homeostatic adaptation to chronic M-channel modulation. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 972023. |
| 34302896 | not listed | da Silva, T.F., et al. 2021. Plasmalogens regulate the AKT-ULK1 signaling pathway to control the position of the axon initial segment. Progress in Neurobiology, 102123. |
| 32277041 | 1:500 | Lezmy, J., et al. 2020. M-current inhibition in hippocampal excitatory neurons triggers intrinsic and synaptic homeostatic responses at different temporal scales. Journal of Neuroscience, 3694-3706. |
| 31532918 | 1:100 | Di Re, J., et al. 2019. Imaging of the Axon Initial Segment. Current Protocols in Neuroscience, e78. |
| 27044086 | 1:500 | Pablo, J.L., et al. 2016. Polarized localization of voltage-gated Na+ channels is regulated by concerted FGF13 and FGF14 action. PNAS: USA, E2665-2674. |
| 23831029 | 1:500 | Yan, H., et al. 2013. FGF14 regulates presynaptic Ca2+ channels and synaptic transmission. Cell Reports, 66-75. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 26917740 | 1:100 | Hsu, W.C.J., et al. 2016. CK2 activity is required for the interaction of FGF14 with voltage-gated sodium channels and neuronal excitability. FASEB Journal, 2171-2186. |
| 20543823 | 1:500 | Grubb, M.S., et al. 2010. Activity-dependent relocation of the axon initial segment fine-tunes neuronal excitability.. Nature, 1070-1074. |
| 17978045 | 1:1000 | Laezza, F., et al. 2007. The FGF14(F145S) mutation disrupts the interaction of FGF14 with voltage-gated Na+ channels and impairs neuronal excitability.. Journal of Neuroscience, 12033-12044. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Human | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 24107939 | 1:1000 | Puthussery, T., et al. 2013. NaV1. 1 channels in axon initial segments of bipolar cells augment input to magnocellular visual pathways in the primate retina. . Journal of Neuroscience, 16045-16059. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 31933626 | 1:300 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2019. Changes in the Fluorescence Tracking of NaV1.6 Protein Expression in a BTBR T+Itpr3tf/J Autistic Mouse Model. Neural Plasticity, 4893103. |
| 31532918 | 1:300 | Di Re, J., et al. 2019. Imaging of the Axon Initial Segment. Current Protocols in Neuroscience, e78. |
| 29359916 | 1:300 | Ali, S.R., et al. 2018. Functional Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by a FGF14-Based Peptidomimetic. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 976-987. |
| 29109270 | 1:500 | Lezmy, J., et al. 2017. M-current inhibition rapidly induces a unique CK2-dependent plasticity of the axon initial segment. PNAS: USA, E10234-E10243. |
| 28522250 | 1:400 | Hsu, W.C.J., et al. 2017. PPARgamma agonists rescue increased phosphorylation of FGF14 at S226 in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Experimental Neurology, 1-17. |
| 27044086 | 1:500 | Pablo, J.L., et al. 2016. Polarized localization of voltage-gated Na+ channels is regulated by concerted FGF13 and FGF14 action. PNAS: USA, E2665-2674. |
| 26909021 | 1:300 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2016. Improved methods for fluorescence microscopy detection of macromolecules at the axon initial segment. . Frontiers in cellular neuroscience, 5. |
| 26687232 | 1:300 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2016. Fibroblast growth factor 14 modulates the neurogenesis of granule neurons in the adult dentate gyrus. Molecular Neurobiology, 7254-7270. |
| 25926453 | 1:1000 | Bosch, M.K., et al. 2015. Intracellular FGF14 (iFGF14) Is Required for Spontaneous and Evoked Firing in Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons and for Motor Coordination and Balance.. Journal of Neuroscience, 6752-69. |
| 25653382 | not listed | Baalman, K., et al. 2015. Axon initial segment-associated microglia.. Journal of Neuroscience, 2283-2292. |
| 25093726 | 1:1000 | , et al. 2014. Dual transgene expression in murine cerebellar Purkinje neurons by viral transduction in vivo.. PLoS One, e104062. |
| 23891806 | 1:1000 | Xiao, M., et al. 2013. FGF14 localization and organization of the axon initial segment. . Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 393-403. |
| 22131424 | not listed | Kaphzan, H., et al. 2011. Alterations in intrinsic membrane properties and the axon initial segment in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome.. Journal of Neuroscience, 17637-17648. |
| 19073816 | 2ug/ml | Diwakar, S., et al. 2009. Axonal Na+ channels ensure fast spike activation and back-propagation in cerebellar granule cells.. Journal of Neurophysiology, 519-532. |
| 18930825 | 1:1000 | Shakkottai, V.G., et al. 2008. FGF14 regulates the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar Purkinje neurons.. Neurobiology of Disease, 81-88. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Non-Human Primate | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 24107939 | 1:1000 | Puthussery, T., et al. 2013. NaV1. 1 channels in axon initial segments of bipolar cells augment input to magnocellular visual pathways in the primate retina. . Journal of Neuroscience, 16045-16059. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 25724910 | 1:100 | Wildburger, N.C., et al. 2015. Quantitative proteomics reveals protein–protein interactions with fibroblast growth factor12 as a component of the Nav1. 2 macromolecular complex in …. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 1288-1300. |
| Immunoprecipitation: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 27666389 | 1ug/ml | Dover, K., et al. 2016. FHF-independent conduction of action potentials along the leak-resistant cerebellar granule cell axon. Nature Communications, 12895. |
| 26889602 | not listed | Bosch, M.K., et al. 2016. Proteomic analysis of native cerebellar iFGF14 complexes.. Channels, 297-312. |
| 25269146 | 2ug | Yan, H., et al. 2014. FGF14 modulates resurgent sodium current in mouse cerebellar Purkinje neurons.. Elife, e04193. |
| Western Blot: Human | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 25854634 | 1:1000 | Duarri, A., et al. 2015. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 19/22 mutations alter heterocomplex Kv4. 3 channel function and gating in a dominant manner. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 3387-3399. |
| Western Blot: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 31933626 | 1:500 | Alshammari, M.A., et al. 2019. Changes in the Fluorescence Tracking of NaV1.6 Protein Expression in a BTBR T+Itpr3tf/J Autistic Mouse Model. Neural Plasticity, 4893103. |
| 25093726 | 1:1000 | , et al. 2014. Dual transgene expression in murine cerebellar Purkinje neurons by viral transduction in vivo.. PLoS One, e104062. |