Anti-Amyloid beta peptide (A-beta 40/42) Antibody (MOAB-2)
Our Anti-Amyloid beta peptide (A-beta 40/42) mouse monoclonal primary antibody detects human and rat Amyloid beta peptide (A-beta 40/42), and is IgG. It is validated for use in ELISA, FC, ICC, IHC-Frozen, IHC-Paraffin-embedded, IP, WB.

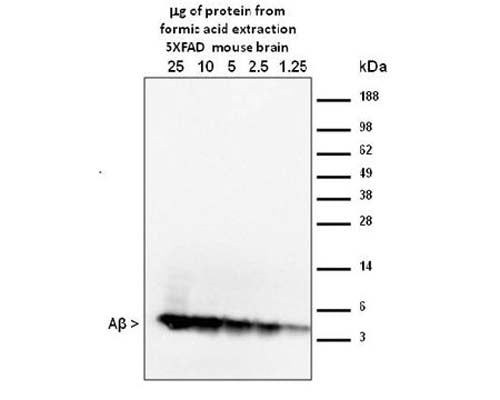
Sample combined cortex and hippocampus from 12 month old 5xFAD mice. 1.25-25 mg of FA extraction were analyzed using the standard Western blot procedure as described in Youmans, Molecular Neurodegeneration, 2012. MOAB-2 was used at a concentration of 1 µg/mL.
Extraction protocol: Modified 3-step sequential extraction as described in Youmans et al, J Neurosci Methods, 2011.The modification involved using less volume of formic acid (FA) in step 3 to give a more concentrated extraction. Therefore, 70% FA was added at to a concentration of 600 mg/mL rather than 150 mg/mL as described in Youmans et al. The final protein concentration of the neutralized formic acid extraction was 0.9 mg/mL
Youmans, KL et al (2011) J. Neuroscience Methods 196(1):51-59. PMID: 21219931.
Youmans, KL et al (2012) Mol. Neurodegener. PMID: 22423893.
Click on image to zoom
Extraction protocol: Modified 3-step sequential extraction as described in Youmans et al, J Neurosci Methods, 2011.The modification involved using less volume of formic acid (FA) in step 3 to give a more concentrated extraction. Therefore, 70% FA was added at to a concentration of 600 mg/mL rather than 150 mg/mL as described in Youmans et al. The final protein concentration of the neutralized formic acid extraction was 0.9 mg/mL
Youmans, KL et al (2011) J. Neuroscience Methods 196(1):51-59. PMID: 21219931.
Youmans, KL et al (2012) Mol. Neurodegener. PMID: 22423893.
SKU: M-1586-100
Ships: 1-2 business days
Product Details
Amyloid beta peptide (A-beta 40/42)
The amyloid beta peptide is derived from the cleavage of the Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and varies in length from 39 to 43 amino acids. However, the form(s) of amyloid-beta peptide (Aβ associated with the pathology characteristic of Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains unclear. In particular, the neurotoxicity of intraneuronal Aβ accumulation is an area of considerable research and controversy principally because antibodies thought to be specific for Aβ have been shown to actually detect intraneuronal APP and not Aβ exclusively.
MOAB-2 (mouse IgG2b) is a pan-specific, high-titer antibody to Aβ residues 1-4 as demonstrated by biochemical and immunohistochemical analyses (IHC), and is highly specific just to amyloid beta peptide.
MOAB-2 did not detect APP or APP-CTFs in cell culture media/lysates (HEK-APPSwe or HEK APPSwe/BACE1) or in brain homogenates from transgenic mice expressing 5 familial AD (FAD) mutation (5xFAD mice).
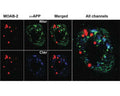
Using IHC on 5xFAD brain tissue, MOAB-2 immunoreactivity co-localized with C-terminal antibodies specific for Aβ40 and Aβ42. MOAB-2 did not co-localize with either N- or C-terminal antibodies to APP. In addition, no MOAB-2-immunreactivity was observed in the brains of 5xFAD/BACE-/- mice, although significant amounts of APP were detected by N- and C-terminal antibodies to APP, as well as by 6E10.
In both 5xFAD and 3xTg mouse brain tissue, MOAB-2 co-localized with cathepsin-D, a marker for acidic organelles, further evidence for intraneuronal Aβ, distinct from Aβ associated with the cell membrane. MOAB-2 demonstrated strong intraneuronal and extra-cellular immunoreactivity in 5xFAD and 3xTg mouse brain tissues.
MOAB-2 (mouse IgG2b) is a pan-specific, high-titer antibody to Aβ residues 1-4 as demonstrated by biochemical and immunohistochemical analyses (IHC), and is highly specific just to amyloid beta peptide.
MOAB-2 did not detect APP or APP-CTFs in cell culture media/lysates (HEK-APPSwe or HEK APPSwe/BACE1) or in brain homogenates from transgenic mice expressing 5 familial AD (FAD) mutation (5xFAD mice).
Using IHC on 5xFAD brain tissue, MOAB-2 immunoreactivity co-localized with C-terminal antibodies specific for Aβ40 and Aβ42. MOAB-2 did not co-localize with either N- or C-terminal antibodies to APP. In addition, no MOAB-2-immunreactivity was observed in the brains of 5xFAD/BACE-/- mice, although significant amounts of APP were detected by N- and C-terminal antibodies to APP, as well as by 6E10.
In both 5xFAD and 3xTg mouse brain tissue, MOAB-2 co-localized with cathepsin-D, a marker for acidic organelles, further evidence for intraneuronal Aβ, distinct from Aβ associated with the cell membrane. MOAB-2 demonstrated strong intraneuronal and extra-cellular immunoreactivity in 5xFAD and 3xTg mouse brain tissues.
IgG
Monoclonal
MOAB-2
ELISA, Flow, ICC, IHC, IP, WB
Mouse
Recombinant human amyloid beta protein 42 (Aβ42): DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKLVFFAEDVGSNKGAIIGLMVGGVVIA
Human
Human, Rat
Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute in 100 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material. Final buffer is 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, 0.01% sodium azide, 0.1% trehalose, pH 7.2.After reconstitution keep aliquots at -20°C to -70°C for a higher stability. At 2-8°C keep up to one week, insulated, protected from light; use sterile methods and pipettes. Highly purified glycerol (1:1) may be added for an additional stability. Avoid repetitive freeze/thaw cycles. Keep tightly closed when not in use and protected from light.
Lyophilized
This product is a Protein A purified mouse IgG2b in 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, 0.01% sodium azide, pH 7.2.
WB: 1:2000-1:5000
IHC: 1:50-1:1000
IP: 1:200-1:1000
ELISA: 1:50-1:1000
IHC: 1:50-1:1000
IP: 1:200-1:1000
ELISA: 1:50-1:1000
Antibody has been tested in WB using purified synthetic beta-amyloid preparations and from transgenic mouse brain formic acid extracts. Formic acid extraction/concentration is required for Western blot detection from extracts. MOAB-2 antibody is specific for beta-amyloid and does not detect APP. Detection of beta-amyloid 40/42 in direct Westerns can be difficult; Dot-blots of prepared samples are recommended as detailed in Youmans. KL et al 2012.
IR or fluorescent detection systems not yet tested, they but are expected to work well with higher primary antibody dilutions because of the increased sensitivity of the detection methods.
For IHC, Antibody was tested on 4% paraformaldehyde/0.1% glutaraldehyde fixed frozen tissue from 3xTg and 5xFAD mice. MOAB-2 antibody detects intraneuronal and extracellular beta-amyloid in IHC and does not detect APP {Youmans KL et al 2012}.
The antibody also reacts with archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples with antigen Heat Induced Epitope Retrieval (HIER): Recommended Citrate, pH 6.0 buffer for HIER. Signal was weak without antigen retrieval. Immunoreactively was expressed in intraneural-amyloid deposition (plaque) in Alzheimer's brain. MoAB-2 was found to be extremely clean and with an excellent signal to noise ratio with no neuro-cellular diffusive staining.
In addition MOAB-2 demonstrated no significant differences in A-beta detection using paraffin fixed, free-floating sections {Youmans KL et al 2012}. Formic acid (FA) treatment resulted in optimal detection of both intraneuronal and extracellular A-beta compared to without FA (incubated in 88% FA 8 min, Youmans KL et al 2012). Free floating tissue sections were permeabilized in TBS containing 0.25% Triton X-100 (TBSX; 3 x 10 min), blocked with 3% horse serum in TBSX (3 x 10 min) followed by 1% horse serum in TBSX (2 x10 min) and incubated with appropriate primary antibodies diluted in TBSX containing 1% horse serum overnight. See Youmans KL et al 2012 for full IH(P) protocol and method details.
For IF, suggested dilution is 1:100-1:500. The antibody was tested on 4% PFA fixed frozen tissue. Fixed tissues were washed in TBS (3 x 10 min), then incubated in 88% FA (8 min), and then permeabilized in TBSX (3 x 10 min), and blocked in TBSX containing 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA; 1 hr). Sections were subsequently incubated with appropriate primary antibodies diluted in TBSX containing 2% BSA overnight on an oscillatory rotator. Detection was via fluorescently labelled absorbed secondary antibodies {Youmans KL et al 2012}.
For IP, the suggested dilution is 1:200 to 1:1000 for labeled beta-amyloid using Protein A/G conjugated beads as the capture vehicle {Youmans KL et al 2012}.
In an ELISA, a dilution of 1:50-1:1000 is suggested. The antibody has been tested in ELISAs on synthetic beta-amyloid and tissue homogenates from beta-amyloid-Tg mice.
IR or fluorescent detection systems not yet tested, they but are expected to work well with higher primary antibody dilutions because of the increased sensitivity of the detection methods.
For IHC, Antibody was tested on 4% paraformaldehyde/0.1% glutaraldehyde fixed frozen tissue from 3xTg and 5xFAD mice. MOAB-2 antibody detects intraneuronal and extracellular beta-amyloid in IHC and does not detect APP {Youmans KL et al 2012}.
The antibody also reacts with archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples with antigen Heat Induced Epitope Retrieval (HIER): Recommended Citrate, pH 6.0 buffer for HIER. Signal was weak without antigen retrieval. Immunoreactively was expressed in intraneural-amyloid deposition (plaque) in Alzheimer's brain. MoAB-2 was found to be extremely clean and with an excellent signal to noise ratio with no neuro-cellular diffusive staining.
In addition MOAB-2 demonstrated no significant differences in A-beta detection using paraffin fixed, free-floating sections {Youmans KL et al 2012}. Formic acid (FA) treatment resulted in optimal detection of both intraneuronal and extracellular A-beta compared to without FA (incubated in 88% FA 8 min, Youmans KL et al 2012). Free floating tissue sections were permeabilized in TBS containing 0.25% Triton X-100 (TBSX; 3 x 10 min), blocked with 3% horse serum in TBSX (3 x 10 min) followed by 1% horse serum in TBSX (2 x10 min) and incubated with appropriate primary antibodies diluted in TBSX containing 1% horse serum overnight. See Youmans KL et al 2012 for full IH(P) protocol and method details.
For IF, suggested dilution is 1:100-1:500. The antibody was tested on 4% PFA fixed frozen tissue. Fixed tissues were washed in TBS (3 x 10 min), then incubated in 88% FA (8 min), and then permeabilized in TBSX (3 x 10 min), and blocked in TBSX containing 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA; 1 hr). Sections were subsequently incubated with appropriate primary antibodies diluted in TBSX containing 2% BSA overnight on an oscillatory rotator. Detection was via fluorescently labelled absorbed secondary antibodies {Youmans KL et al 2012}.
For IP, the suggested dilution is 1:200 to 1:1000 for labeled beta-amyloid using Protein A/G conjugated beads as the capture vehicle {Youmans KL et al 2012}.
In an ELISA, a dilution of 1:50-1:1000 is suggested. The antibody has been tested in ELISAs on synthetic beta-amyloid and tissue homogenates from beta-amyloid-Tg mice.
Unconjugated
MOAB-2 detects preparations enriched in U-, O-, F-Aβ42, and U-Aβ40 by dot-blot, and is thus a pan-specific Aβ antibody. However, MOAB-2 is selective for the more neurotoxic Aβ42 compared to Aβ40. Indeed, MOAB-2 demonstrated a titration against antigen concentration, and detects Aβ40 at 2.5 pmol but U-, O- and FAβb42 at antigen concentrations as low as ~ 0.1 pmol {Youmans. KL et al 2012}. MOAB-2 does not detect APP (Amyloid precursor protein). Human, rat, other species not yet tested.By Dot blot, MOAB-2 detected rat Aβ40 and human Aβ40, albeit with less affinity than for Aβ42. {Youmans. KL et al 2012}.
For research use only.
United States
12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
Beta-APP42; Beta-APP40; Beta-amyloid protein 42; Beta-amyloid protein 40; ABPP; APPI; Amyloid beta A4 protein;MOAB2;MOAB-2; Alzheimer's antibody;AB40;AB42;abeta
25°C (ambient)