Ships: 1-2 business days
Product Specific References for Applications and Species
- Electron Microscopy: Mouse
- Immunocytochemistry: Rat
- Immunohistochemistry: Mouse | Rat
- Immunoprecipitation: Mouse
- Western Blot: Mouse | Rat | Xenopus
| Electron Microscopy: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28943756 | 1:500 | Tomasello, D.L., et al. 2017. Slick (Kcnt2) Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Limit Peptidergic Nociceptor Excitability and Hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, . |
| Immunocytochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28943756 | 1:500 | Tomasello, D.L., et al. 2017. Slick (Kcnt2) Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Limit Peptidergic Nociceptor Excitability and Hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, . |
| 28660246 | 1:50 | Li, P., et al. 2017. GABA-B Controls Persistent Na+ Current and Coupled Na+-Activated K+ Current. eNeuro, . |
| 27091544 | 1:50 | Bansal, V., et al. 2016. Na(+) -Activated K(+) Channels in Rat Supraoptic Neurones. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, . |
| Immunohistochemistry: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28943756 | 1:250 | Tomasello, D.L., et al. 2017. Slick (Kcnt2) Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Limit Peptidergic Nociceptor Excitability and Hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, . |
| 29124216 | 1:200 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2015. Identification of potential novel interaction partners of the sodium-activated potassium channels Slick and Slack in mouse brain. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 291-298. |
| Immunohistochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 38600344 | 1:200 | Wang, K, et al. 2024. Circular RNA-GRIN2B Suppresses Neuropathic Pain by Targeting the NF-κB/SLICK Pathway. Neuromolecular Medicine, 12. |
| 23466807 | 1:1000 | Cervantes, B., et al. 2013. Identity, expression and functional role of the sodium-activated potassium current in vestibular ganglion afferent neurons.. Neuroscience, 163-175. |
| 19403831 | 1.5ug/ml | Chen, H., et al. 2009. The N-terminal domain of Slack determines the formation and trafficking of Slick/Slack heteromeric sodium-activated potassium channels. Journal of Neuroscience, 5654-5665. |
| Immunoprecipitation: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 29124216 | 40ug | Rizzi, S., et al. 2015. Identification of potential novel interaction partners of the sodium-activated potassium channels Slick and Slack in mouse brain. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 291-298. |
| 26559620 | not listed | Martinez-Espinosa, P.L., et al. 2015. Knockout of Slo2.2 enhances itch, abolishes KNa current, and increases action potential firing frequency in DRG neurons.. Elife, . |
| Western Blot: Mouse | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 35303056 | 1:500 | Flauaus, C., et al. 2022. Slick Potassium Channels Control Pain and Itch in Distinct Populations of Sensory and Spinal Neurons in Mice. Anesthesiology, 802-822. |
| 28943756 | 1:1000 | Tomasello, D.L., et al. 2017. Slick (Kcnt2) Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Limit Peptidergic Nociceptor Excitability and Hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, . |
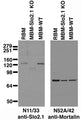
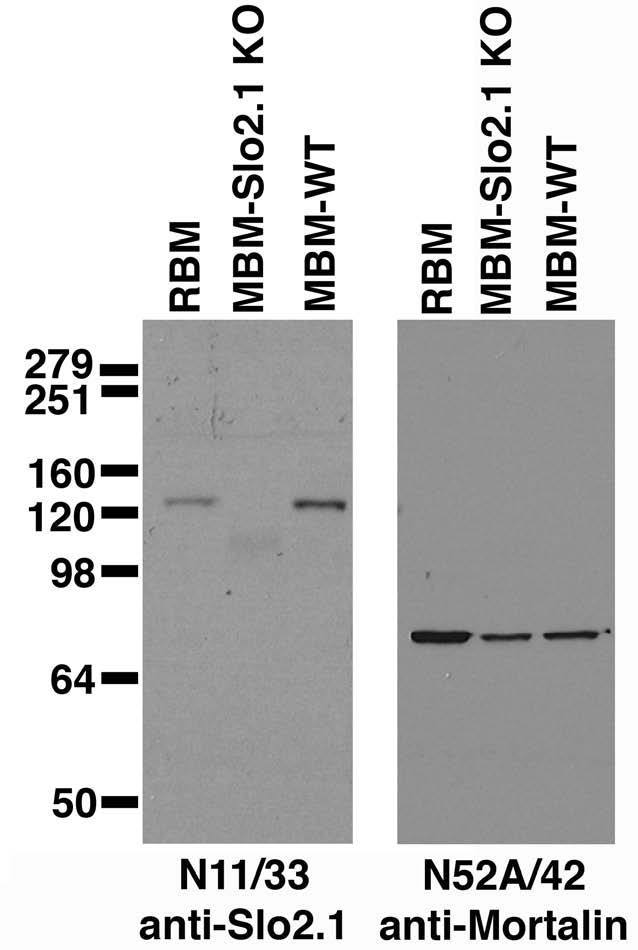
| 26845140 | not listed | Wojtovich, A.P., et al. 2016. Cardiac Slo2.1 Is Required for Volatile Anesthetic Stimulation of K+ Transport and Anesthetic Preconditioning.. Anesthesiology, 1065-1076. |
| 26587966 | 1:3000 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2016. Differential distribution of the sodium-activated potassium channels slick and slack in mouse brain.. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 2093-2116. |
| 29124216 | 1:1000 | Rizzi, S., et al. 2015. Identification of potential novel interaction partners of the sodium-activated potassium channels Slick and Slack in mouse brain. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 291-298. |
| 26559620 | not listed | Martinez-Espinosa, P.L., et al. 2015. Knockout of Slo2.2 enhances itch, abolishes KNa current, and increases action potential firing frequency in DRG neurons.. Elife, . |
| 22145034 | not listed | Wojtovich, A.P., et al. 2011. SLO-2 is cytoprotective and contributes to mitochondrial potassium transport.. PLoS One, e28287. |
| Western Blot: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 38600344 | 1:500 | Wang, K, et al. 2024. Circular RNA-GRIN2B Suppresses Neuropathic Pain by Targeting the NF-κB/SLICK Pathway. Neuromolecular Medicine, 12. |
| 27091544 | 1:500 | Bansal, V., et al. 2016. Na(+) -Activated K(+) Channels in Rat Supraoptic Neurones. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, . |
| Western Blot: Xenopus | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 29069600 | not listed | Gururaj, S., et al. 2017. A De Novo Mutation in the Sodium-Activated Potassium Channel KCNT2 Alters Ion Selectivity and Causes Epileptic Encephalopathy. Cell Reports, 926-933. |