Anti-Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Antibody
Our Anti-Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) rabbit polyclonal primary antibody detects human, mouse, other mammals (predicted), and rat Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and is whole serum. It is validated for use in IHC-Frozen, Neutralization, WB.
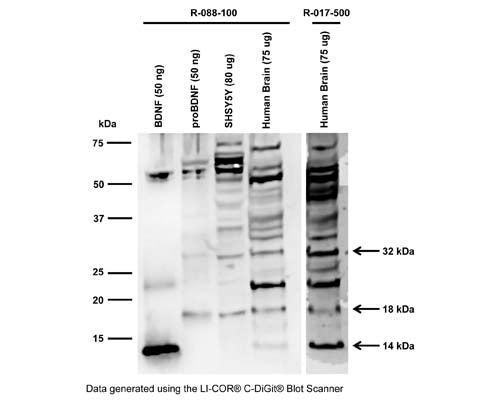
Western blot analysis of BDNF expression in SH-SY5Y cell lysate (RIPA) and human brain. Polyclonal rabbit antibodies to rhBDNF R-088-100 (whole serum, 1:1000) and R-017-500 (IgG, 10 µg/mL) detect monomeric BDNF at 14 kDa in human brain (Tris-homogenate). ProBDNF is detected at the expected molecular weight of 32 kDa for glycosylated proBDNF monomer. A 18 kDa BDNF-isoform is shown that has previously been detected with other BDNF antibodies (Tongiorgi et al., 2012; Silhol et al., 2017). This 18 kDa band is also visible in the proBDNF protein sample, Lane 2.
Western Blotting Method: SDS-PAGE: denaturing and reducing, 12% Bis-Tris gel; Transfer: Tris-Glycine buffer, semi-dry transfer; Membrane: nitrocellulose (0.22 µm); Blocking: 5% skim milk in TBST, 1 hour at RT; Primary antibody: overnight at 4°C; Secondary antibody: anti-rabbit-HRP (1/6000), 2 hours at RT; Detection: Chemiluminiscence.
Click on image to zoom
Western Blotting Method: SDS-PAGE: denaturing and reducing, 12% Bis-Tris gel; Transfer: Tris-Glycine buffer, semi-dry transfer; Membrane: nitrocellulose (0.22 µm); Blocking: 5% skim milk in TBST, 1 hour at RT; Primary antibody: overnight at 4°C; Secondary antibody: anti-rabbit-HRP (1/6000), 2 hours at RT; Detection: Chemiluminiscence.
SKU: R-088-100
Product Details
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
BDNF belongs to the neurotrophin family and regulates the survival and differentiation of neurons during development. The alterations in BDNF expression induced by various kinds of brain insult including stress, ischemia, seizure activity and hypoglycemia, may contribute to some pathologies such as depression, epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease. Microglia release BDNF that may contribute to neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. FUNCTION: Promotes the survival of neuronal populations that are all located either in the central nervous system or directly connected to it. Major regulator of synaptic transmission and plasticity at adult synapses in many regions of the CNS. The versatility of BDNF is emphasized by its contribution to a range of adaptive neuronal responses including long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD), certain forms of short-term synaptic plasticity, as well as homeostatic regulation of intrinsic neuronal excitability. SUBUNIT: Monomers and homodimers. Binds to NTRK2/TRKB. SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted protein. Post Translation Modification (PTM): The propeptide is N-glycosylated and glycosulfated. PTM: Converted into mature BDNF by plasmin (PLG) (By similarity). DISEASE: Defects in BDNF are a cause of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS); also known as congenital failure of autonomic control or Ondine curse. CCHS is a rare disorder characterized by abnormal control of respiration in the absence of neuromuscular or lung disease, or an identifiable brain stem lesion. A deficiency in autonomic control of respiration results in inadequate or negligible ventilatory and arousal responses to hypercapnia and hypoxemia. CCHS is frequently complicated with neurocristopathies such as Hirschsprung disease that occurs in about 16% of CCHS cases. SIMILARITY: Belongs to the NGF-beta family.
Whole serum
Polyclonal
Mixed
IHC, Neutralize, WB
Rabbit
14, 18, 32 kDa (see application details)
Recombinant human BDNF
Human
Human, Mouse, Rat
Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute in 100 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material. After reconstitution keep aliquots at -20°C for a higher stability, and at 2-8°C with an appropriate antibacterial agent. Avoid repetitive freeze/thaw cycles. Glycerol (1:1) may be added for an additional stability.
Lyophilized
WB: 1:1000
IHC: 1:1000
ELISA: 1:1000
IHC: 1:1000
ELISA: 1:1000
Inhibition of biological activity in vitro/in vivo: 1:10 to 1:50 for inhibition of biological activity in vitro. Use neat for in vivo studies at 5-10 uL/g body weight. This antiserum stains cell bodies and some nerve terminals in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord, however, does not stain finest nerve terminals.
Western Blotting: Antibody does detect BDNF forms in tissue lysates but there are multiple bands present, many of which are uncharacterized. The antibody detects 14 kDa (mature BDNF), 32 kDa (proBDNF) and a 18 kDa BDNF isoform (see blot examples). In cell lysates, only 18 kDa and 32 kDa BDNF are detected. The reason for these differences has not been characterized. Alternative antibodies for Western Blotting are: R-017-500 (IgG-purified form of R-088-100 for tissue homogenate analysis); R-1707-100 (cell lysates and tissue homogenates), R-083-100/R-066-500 (cell lysates, tissue homogenates and human serum); M-1744-50/100 (human serum and tissue homogenates).
Western Blotting: Antibody does detect BDNF forms in tissue lysates but there are multiple bands present, many of which are uncharacterized. The antibody detects 14 kDa (mature BDNF), 32 kDa (proBDNF) and a 18 kDa BDNF isoform (see blot examples). In cell lysates, only 18 kDa and 32 kDa BDNF are detected. The reason for these differences has not been characterized. Alternative antibodies for Western Blotting are: R-017-500 (IgG-purified form of R-088-100 for tissue homogenate analysis); R-1707-100 (cell lysates and tissue homogenates), R-083-100/R-066-500 (cell lysates, tissue homogenates and human serum); M-1744-50/100 (human serum and tissue homogenates).
Unconjugated
Less than 0.1% cross-reactivity against NGF, NT3 and NT4/5 by dot blot. Known to react with BDNF from rat, mouse and human. Expected to react with BDNF from other species due to amino acid sequence homology.
For research use only.
United States
12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Abrineurin; proBDNF;
25°C (ambient)