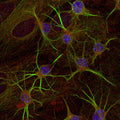
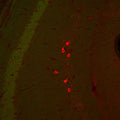
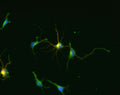
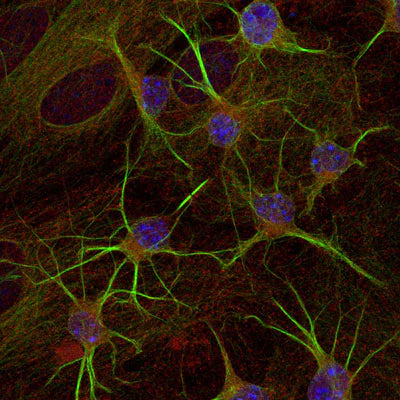
Anti-Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase-67 (GAD 67) Antibody
This affinity-purified antipeptide antibody was generated in chickens against a sequence shared between the mouse (CAA01912) and human (NP_000808) gene products.
SKU: GAD
Ships: 1-2 business days
Product Details
Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase-67 (GAD 67)
Human Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase (GAD-67), [EC 4.1.1.15] is a 66,987 dalton protein (594 amino acids) selectively expressed in a subpopulation of GABAergic neurons of the CNS. It catalyzes the decarboxylation of glutamic acid, forming the inhibitory neurotransmitter beta-amino butyric acid (GABA). It is also know as GAD-1.
Affinity-Purified IgY
100 µg/mL
Polyclonal
IgY
ICC, IHC, WB
Chicken
GAD1 GAD GAD67
67 kDa
Synthetic peptide
Human
Human, Mouse, Rat
AB_2313545
Store at 4°C in the dark. Under these conditions, the antibodies should have a shelf life of at least twelve months, provided they remain sterile. For longer term storage, aliquot and freeze to avoid freeze-thaw of the antibody.
Liquid
Chickens were immunized with a synthetic peptide / keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) conjugate. This synthetic peptide corresponded to a region near the Cterminus of this gene product, and was 100% conserved between the human (Q99259, NCBI), mouse (P48318, NCBI) and rat (NP_058703, NCBI) gene products. After repeated injections into the hens, immune eggs were collected, and the IgY fractions were purified from the yolks. These IgY fractions were then affinity-purified using a peptide column, the concentrations of the eluate adjusted to 100 µg/mL, and the preparation was filter-sterilized through a 0.45 µm filter.
Phosphate-buffered (10 mM) isotonic (0.9%, w/v) saline (“PBS," pH 7.2) with sodium azide (0.02%, w/v) added as a preservative.
WB: 1:1000-1:2000
IHC: 1:500-1:1000
ICC: 1:500-1:1000
IHC: 1:500-1:1000
ICC: 1:500-1:1000
This antibody preparation was analyzed by immunohisto-chemistry (at a concentration of 1 µg/mL) using fluorescein-labeled goat anti-chicken IgY (1:500 dilution, Aves Labs Cat.# F-1005) as the secondary reagent.
These antibodies are to be used as research laboratory reagents and are not for use as diagnostic or therapeutic reagents in humans.
United States
12 months from receipt of product
Glutamate decarboxylase 1 (EC 4.1.1.15) (67 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase) (GAD-67) (Glutamate decarboxylase 67 kDa isoform)
Ice packs
Product Specific References for Applications and Species
| Immunocytochemistry: Human | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28377585 | 1:2000 | Bigler, R.L., et al. 2017. Messenger RNAs localized to distal projections of human stem cell derived neurons. Nature Scientific Reports, 611. |
| Immunocytochemistry: Rat | ||
| PMID | Dilution | Publication |
| 28931811 | 1:2000 | Nagendran, T., et al. 2017. Distal axotomy enhances retrograde presynaptic excitability onto injured pyramidal neurons via trans-synaptic signaling. Natrue Communications, 625. |