Anti-Sortilin Antibody
Our Anti-Sortilin rabbit polyclonal primary antibody detects human, mouse, and rat Sortilin, and is whole serum. It is validated for use in ELISA, IHC-Frozen.
SKU: R-150-100
Product Details
Sortilin
FUNCTION: Functions as a sorting receptor in the Golgi compartment and as a clearance receptor on the cell surface. Required for protein transport from the Golgi apparatus to the lysosomes by a pathway that is independent of the mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6PR). Also required for protein transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endosomes. Promotes neuronal apoptosis by mediating endocytosis of the proapoptotic precursor forms of BDNF (proBDNF) and NGFB (proNGFB). Also acts as a receptor for neurotensin. May promote mineralization of the extracellular matrix during osteogenic differentiation by scavenging extracellular LPL. Probably required in adipocytes for the formation of specialized storage vesicles containing the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 (GLUT4 storage vesicles, or GSVs). These vesicles provide a stable pool of SLC2A4 and confer increased responsiveness to insulin. May also mediate transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. SUBUNIT: Interacts with LPL and SLC2A4. Interacts with the cytosolic adapter proteins GGA1 and GGA2. Interacts with numerous ligands including the receptor-associated protein LRPAP1/RAP, GM2A and PSAP. Forms a complex with NGFR which binds specifically to the precursor forms of NGFB (proNGFB) and BDNF (proBDNF). SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Membrane; single-pass type I membrane protein. Localized to membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum, endosomes, Golgi stack, lysosomes and nucleus. A small fraction of the protein is also localized to the plasma membrane. May also be found in SLC2A4/GLUT4 storage vesicles (GSVs) in adipocytes. Localization to the plasma membrane in adipocytes may be enhanced by insulin. TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed at high levels in brain, spinal cord, heart, skeletal muscle, thyroid, placenta and testis. Expressed at lower levels in lymphoid organs, kidney, colon and liver. INDUCTION: During osteoblast differentiation. DOMAIN: The N-terminal propeptide may facilitate precursor transport within the Golgi stack. Intrachain binding of the N-terminal propeptide and the extracellular domain may also inhibit premature ligand binding. DOMAIN: The extracellular domain may be shed following protease cleavage in some cell types. PTM: The N-terminal propeptide is cleaved by furin and possibly other homologous proteases. PTM: Contains 8 intrachain disulfide bonds. PTM: N-glycosylated. SIMILARITY: Contains 9 BNR repeats.
Whole serum
Polyclonal
Mixed
ELISA, IHC
Rabbit
Extracellular domain of glycosylated human sortilin produced in CHO cells was used as the immunogen.
Human
Human, Mouse, Rat
Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute in 100 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material. After reconstitution keep aliquots at -20°C for a higher stability, and at 2-8°C with an appropriate antibacterial agent. Glycerol (1:1) may be added for an additional stability. Avoid repetitive freeze/thaw cycles.
Lyophilized
IHC: 1:1000
ELISA: 1:5000
ELISA: 1:5000
Unconjugated
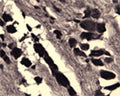
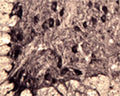
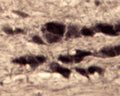
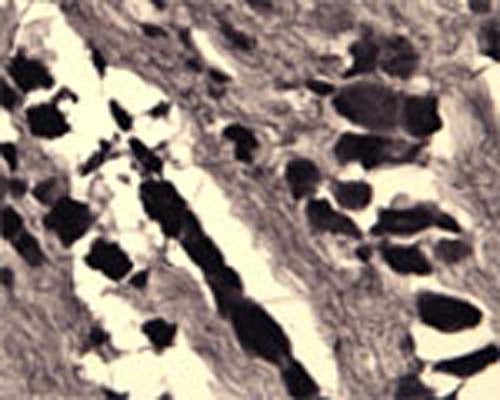
Specificity was demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. Reacts with human, rat and mouse Sortilin. Other species not yet tested.
For research use only.
United States
12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
Neurotensin receptor 3; NTR3; NT3; Glycoprotein 95; Gp95; 100 kDa NT receptor; SORT1;
25°C (ambient)